Working in warehouse operations requires a high emphasis on safety. Injuries to workers and damage to facilities and equipment can quickly result when proper training, procedure, and hygiene aren’t observed. More accidents also means reduced efficiency and productivity, resulting in costly delays or other operational shortfalls that can quickly hurt profitability. Committing to safety involves implementing comprehensive measures and creating a safety culture that is supported across all levels of the organization. By doing so, warehouse owners can not only minimize risks but also promote a sense of well-being among employees. In this article, we will be explaining the importance of warehouse safety and all the things that will help business owners continue to keep their staff safe.
The origins of warehouse safety can be traced back to the Industrial Revolution, a period marked by rapid industrialization and significant workplace hazards. The rapid industrialization during the 19th century led to the construction of large factories and warehouses. Safety standards were virtually non-existent, and workers faced hazardous conditions with little to no protective measures. During this time, the lack of safety measures led to numerous severe injuries and fatalities among workers. The rise of labor movements in the late 19th and early 20th centuries began to address the need for safer working conditions. The 1930s saw the establishment of organizations like the National Safety Council (NSC) in the United States, which played a crucial role in promoting workplace safety through research, education, and advocacy. Over time, new legislation was created to mandate basic safety precautions in the workplace, eventually leading to the Occupational Safety and Health Act in 1970, which established OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration). Today OSHA plays a vital role in enforcing safety standards and advocating for improved working conditions.
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) is a federal agency in the United States responsible for ensuring safe and healthy working conditions for employees. Key functions of OSHA include:
Warehouse safety is crucial for the well-being of employees and the overall success of the business. Every year, thousands of workers in warehouses across the country experience injuries, ranging from minor incidents to severe accidents. According to the U.S. Department of Labor, there are around 5 injuries for every 100 full-time warehouse workers annually. These incidents highlight the importance of implementing and maintaining safety standards in warehouse environments. Here are some key reasons why warehouse safety is so important:
When it comes to warehouse safety, business owners need to be well-versed and proactive in various areas to ensure a secure and efficient working environment. From equipment handling and hazard management to emergency preparedness and employee training, having a wide knowledge and effective implementation of safety protocols will help minimize risks and protect both personnel and assets.
Personal Protective Equipment or PPE, refers to the gear or equipment worn by workers to protect themselves from hazards that could cause injuries in the workplace. PPE is a critical component of workplace safety practices and is often required in environments where hazards cannot be completely eliminated through other means. Common types of PPE include:
Warehouse equipment training is essential for maintaining a safe working environment, where heavy machinery and material handling are routine. Proper training not only helps prevent accidents and injuries but also minimizes damage to goods, ensuring smooth and efficient operations. Business owners can opt to train and certify individuals in-house or utilize third-party training services if they lack the necessary resourcing. Key pieces of equipment that require skilled and trained operators include:
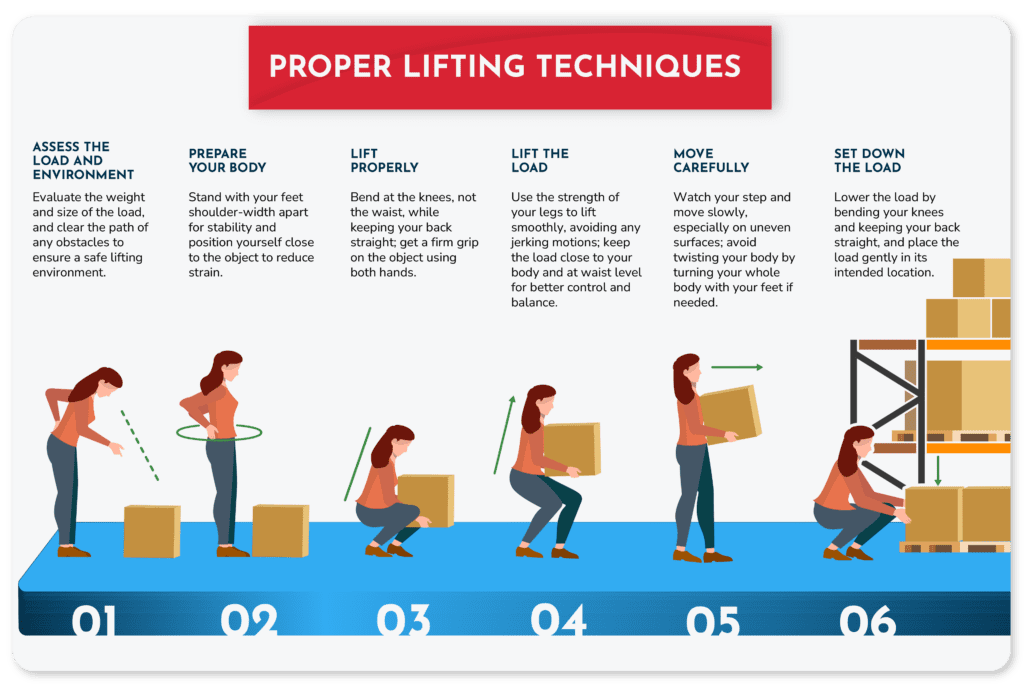
In a warehouse setting, correct lifting techniques are essential to prevent injuries and maintain a safe working environment. By following a proper approach to lifting, workers can reduce the risk of strains and sprains, particularly to the back, shoulders, and arms. Here’s a step-by-step guide to safe lifting:
For heavy or bulky items, warehouse employees should use team lifting techniques or mechanical aids like dollies and carts; regularly participate in training on proper lifting techniques and maintain physical fitness, to further reduce injury risks.
Hazardous materials training in a warehouse is crucial for ensuring the safety of employees and the environment. Proper handling, storage, and disposal of hazardous materials are essential to prevent accidents, injuries, and environmental contamination. Here are key components of hazardous materials training in a warehouse setting:
Ensure training covers relevant regulations from OSHA and the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). Emphasize the importance of accurate documentation, incident reporting, and regulatory compliance.
Implementing best practices for fire safety is crucial for reducing the risk of fire-related incidents in warehouses, which can have devastating effects on both people and property. Warehouses often store a variety of goods, including flammable materials, making them particularly vulnerable to fires. A comprehensive fire safety plan not only protects employees and assets but also ensures compliance with safety regulations. Effective fire safety measures can prevent significant financial losses and operational disruptions, contributing to a safer and more efficient workplace.
Preparing for a natural disaster in a warehouse setting involves planning and implementing procedures to protect employees, secure inventory, and minimize damage to the facility. Proper preparation can significantly reduce the impact of natural disasters such as earthquakes, floods, hurricanes, and tornadoes. Although these can be vastly different, here are key steps to prepare for any natural disasters in a warehouse:
Improving safety procedures in warehouse operations is of utmost importance for protecting employees, reducing accidents, and enhancing overall efficiency. Here are six tips for warehouse owners to enhance safety in their facilities:
Regular safety audits are essential for identifying potential hazards and ensuring that safety protocols are being followed. These audits should be in-depth, covering all aspects of the warehouse, including things like equipment and storage practices. During these inspections, you should involve a team of safety professionals and experienced employees who can provide insights into daily operations. Findings from these audits should be documented, and corrective actions should be taken promptly to address any identified risks.
Proper lighting improves safety and efficiency in a warehouse environment. Poor lighting can lead to accidents, such as trips, falls, or mishandling of materials. Ensuring that all areas, including aisles, loading docks, and workstations, are well-lit helps workers see potential hazards and navigate the space safely. Consider using natural light where possible and supplementing it with well-placed artificial lighting. Regular maintenance of lighting fixtures will help prevent outages and maintain consistent visibility.
Keeping aisles and emergency exits clear of obstructions is a fundamental safety practice. Cluttered aisles can lead to accidents and impact quick evacuation during emergencies. Establish clear policies for the storage and placement of goods, ensuring that items are not left in walkways. Regular inspections should be conducted to check for compliance, and employees should be trained to recognize and report potential obstructions.
Safety signage and labels are essential tools for communicating hazards and safety instructions to employees. Clear and visible signs can prevent accidents by warning workers about dangerous areas, equipment, or materials. Labels should be used to identify hazardous substances and provide information on proper handling and storage. It is important to ensure that all signage complies with regulatory standards and is easily understood by all employees, including those who may not be fluent in the primary language used in the workplace.
Safe operation of equipment, including forklifts, pallet jacks, and conveyor systems, greatly prevents accidents and injuries. Only trained and certified individuals should be allowed to operate such equipment. Regular maintenance checks and inspections are necessary to ensure that all machinery is in good working condition and free from defects that could lead to accidents. Establishing clear operational protocols, such as speed limits and designated operating areas, helps prevent collisions and other incidents.
Building a strong safety culture involves making safety a core value of the organization. This means not only setting policies and procedures but also encouraging a mindset where employees prioritize safety in all aspects of their work. Management should lead by example, demonstrating a commitment to safety and recognizing safe behavior in the workplace. Involving employees in safety planning and decision-making fosters a sense of ownership and responsibility for their own safety and that of their colleagues. Open communication channels should be established for reporting hazards and sharing safety concerns, with the assurance that these reports will be taken seriously and addressed promptly.
Implementing safe warehouse procedures for your team can be as time-consuming as staffing the warehouse positions themselves. Luckily, partnering with Staffing By Starboard allows businesses to concentrate on their core operations while we handle the staffing needs. We tap into a vast pool of qualified candidates to quickly find the right individuals for your specific job requirements. With us, you can leave the stress of staffing behind, confident that we have you covered.
816-659-1544 | customerservice@staffingbystarboard.com | 16100 W 116th St, Lenexa, KS 66219