Employment types have evolved to reflect changes in technology, economic conditions, and labor regulations. From the traditional full-time roles that dominated much of the 20th century to the rise of gig work and flexible arrangements in the 21st century, the landscape of employment has seen significant shifts. Here is a look at how employment types have changed throughout the decades.
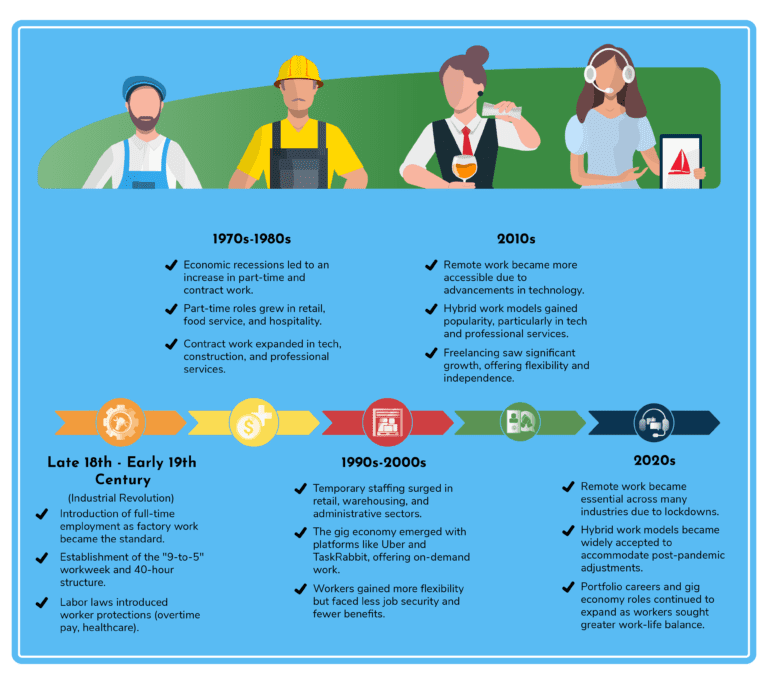
The Industrial Revolution introduced full-time employment as factory work became the standard in many industries. By the mid-20th century, the “9-to-5” workweek and 40-hour structure became normalized in developed nations, particularly in manufacturing and corporate settings. Labor laws also introduced worker protections, creating a stable, long-term work environment for employees. Full-time jobs offered consistent hours, benefits, and job security, becoming the backbone of the workforce for decades.
Key Points:
Economic shifts and recessions in the 1970s and 1980s pushed companies to explore more flexible labor options. Part-time roles grew in industries like retail and hospitality, offering employers lower-cost staffing solutions. At the same time, contract work emerged in sectors requiring specialized skills on a temporary basis. This led to a shift where more employees worked without the long-term security and benefits that full-time employment once guaranteed.
Key Points:
With globalization and technological advances in the 90s and early 2000s, businesses began relying more on temporary workers to fill short-term needs without long-term commitments. Temporary staffing agencies gained popularity in industries like manufacturing and logistics. The gig economy began to emerge with platforms like Uber and TaskRabbit, allowing workers to take on short-term jobs or “gigs” on-demand. These employment types provided flexibility for both workers and employers but lacked the stability and benefits of traditional roles.
Key Points:
As technology advanced in the last decade, remote work became more accessible, particularly in tech, marketing, and professional services. Companies began offering remote and hybrid work options to attract talent and reduce overhead costs. Hybrid models, where employees worked both from home and in-office, became a popular arrangement, particularly in industries that required a mix of collaboration and independent work. Freelancing also saw significant growth, offering more flexibility and independence to workers.
Key Points:
The COVID-19 pandemic fundamentally changed the employment landscape by accelerating the shift to remote work. Many industries had to rapidly adopt remote operations, making this once-niche model the norm. As businesses adjusted post-pandemic, hybrid work became widely accepted, offering flexibility and reducing the need for office space. The gig economy and portfolio careers continued to grow as workers sought more control over their work-life balance. These changes are likely to have a lasting impact on how work is structured moving forward.
Key Points:
Remote work has become a critical component of the modern workplace, offering a range of benefits for both employers and employees. It reshapes traditional work models by providing flexibility, autonomy, and efficiency, all while accommodating the evolving needs of today’s workforce.
Advantages for Employers:
Disadvantages for Employers:
Advantages for Employees:
Disadvantages for Employees:
Hybrid work arrangements combine the best aspects of both remote and in-office work, offering a flexible and balanced approach to modern employment. These arrangements are becoming increasingly important as they support the unique needs of both employees and employers in a changing work landscape. Here are five reasons why hybrid work can be so valuable:
As we look ahead, the employment landscape is set to undergo transformative changes driven by advancements in technology, evolving workforce demands, and global trends. These shifts will redefine how we work, the types of jobs we pursue, and the skills that will be in demand. Here’s how employment is expected to evolve and create exciting new opportunities for workers and businesses alike.

Employers and job seekers both face a common challenge: finding the ideal staffing solution. Navigating the ins and outs of employment on your own can lead to roadblocks, missed opportunities, and untapped potential. At Staffing By Starboard, we offer tailored, expert support to help businesses and candidates alike find the perfect match. With our guidance, you’ll gain access to specialized talent and opportunities, ensuring you always get exactly what you need—no compromises, no dead ends.
Here’s a quick timeline on some of the biggest changes to employment and the workplace throughout the years:
Gig work refers to short-term, flexible jobs typically done by independent contractors or freelancers, often facilitated through digital platforms like Uber, Fiverr, or Upwork. It has become popular because it offers workers significant flexibility and autonomy, allowing them to set their own schedules, choose their tasks, and work as much or as little as they want. Additionally, gig work provides businesses with the ability to access talent on-demand, without the long-term commitments of traditional employment, making it a win-win for both sides.
Finding the right employment type depends on your specific needs, such as work-life balance, benefits, and other important factors. Once you’ve identified what suits you best, you can focus on researching and applying to jobs that align with your preferences.
816-659-1544 | [email protected] | 16100 W 116th St, Lenexa, KS 66219